
This circumstance is used for the use of cooling lubricants in the machining industry.
Urban water is defined by the composition and amount of its dissolved ingredients. This is called the total salt content and is not to be confused with the total hardness of the water. Hardness accounts for only a part of the total salt content. The salt content is determined by conductivity measurement. Basically, the more salt is dissolved, the higher the conductivity.
However, the undesirable salination of the cooling lubricant by dissolved chlorides, sulfates, hardeners, etc. is not only determined by the entry on the city water. Substantial part have evaporation and evaporation losses. Since salts cannot evaporate, they remain in the cooling lubricant and are increasingly concentrated.
An example:
The content of a cooling lubricant circuit after filling is 1000 liters. The total salt content doubles as soon as the contents has evaporated to 500 liters. Refilling with untreated town water leads to further salt entry. The salt load, measurable through the conductance, is increasing steadily.
High salt loads in the coolant cause a number of undesirable effects:
The use of completely desalinated water for the fluid management of cooling lubricants provides a lasting remedy. Demineralized water is also known by the terms deionized, demineralized or simply deionized water. Deionized water contains, with the exception of traces, no dissolved salts. Salinization and negative influence on the manufacturing processes are avoided.

Typically, demineralized water is process water which has a conductivity of less than 10 μS / cm. For comparison - our drinking water generally has conductivities of about 500 S / cm.
It is important to distinguish between the fact that softened water does not correspond in quality to demineralized (DI) water. Softened water from cation exchangers has approximately the same salinity as the original city water. Salination via the make-up is still taking place.
Essentially, two established processes for the production of demineralized process water are currently available for industrial applications: mixed bed ion exchangers and reverse osmosis. Also known by the terms osmosis or simply RO (Reverse Osmosis) system.
Whether a mixed bed exchanger or a RO plant is used depends on how much demineralized water is available in which time. Mixed bed ion exchangers can produce a large amount of demineralized water in a short time. After that they require a chargeable regeneration. Typical application is the short-term filling of a storage container.
This contrasts with the continuous supply of steady amounts of demineralized water. Reverse osmosis systems are more economical here. They do not need to be regenerated. For example, the central automatic supply of one or more machines.
Centrally installed reverse osmosis systems also open up a multitude of additional possibilities. In principle, VE-Water offers two advantages in technical application: It dries without staining and leaves no residue when it evaporates.
Stain-free drying water is indispensable for many surface processes. Keywords:
When water is evaporated, its dissolved salts deposit on the heated surfaces of the evaporators and interfere with heat transfer. Demineralized water fixes the problem. Examples are boiler feed water, steam generators for cleaning and humidification, heating circuits, cooling systems.
Summary:
Saline city water in conjunction with evaporation and evaporation losses in cooling lubricants leads to increasing salinity. High salt contents promote corrosion on the machine and workpiece and increase tool wear. The use of deionized water avoids salination and avoids the above disadvantages.
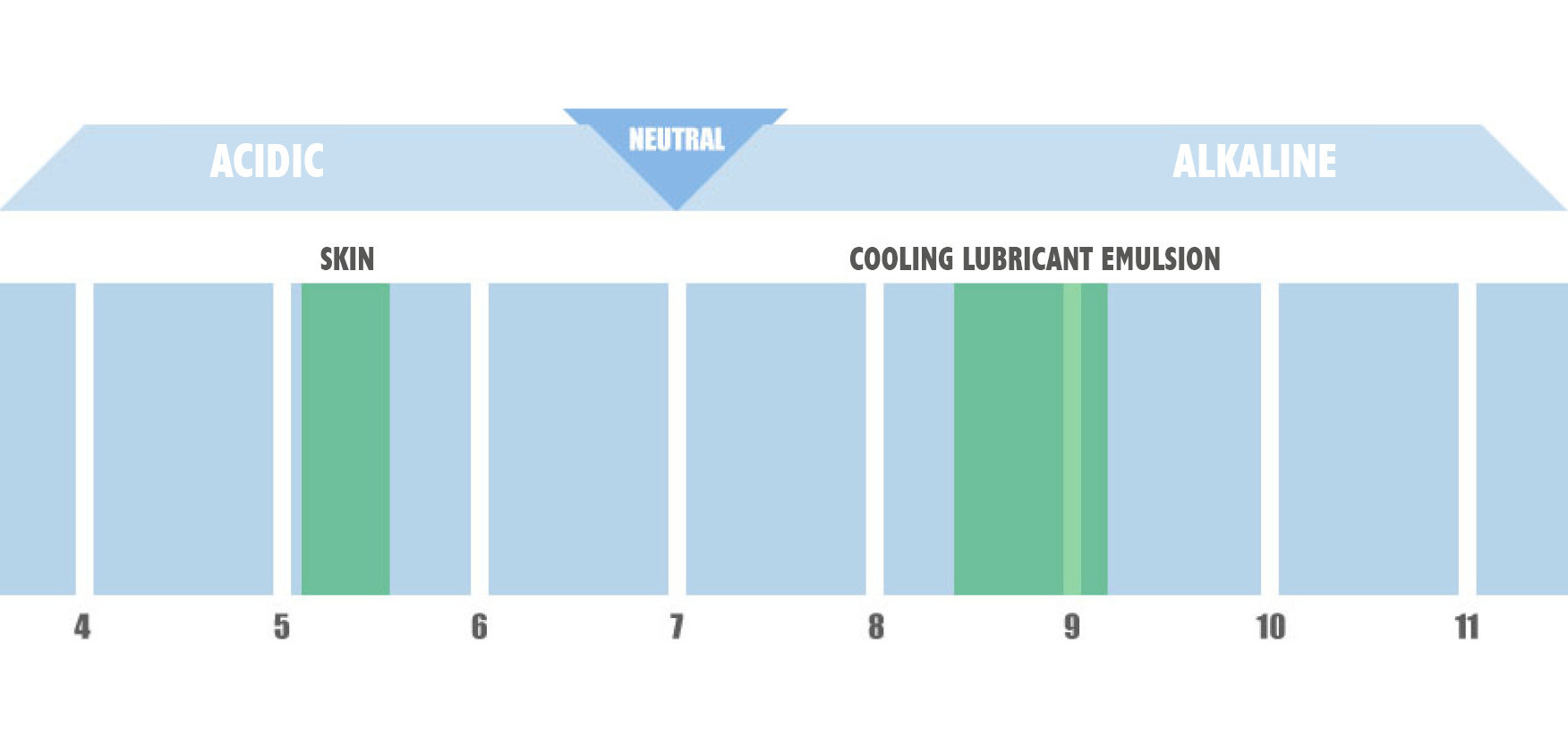
The pH value (pondus Hydrogenii) is the measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions H + contained in a solution (hydronium ions, H3O +).
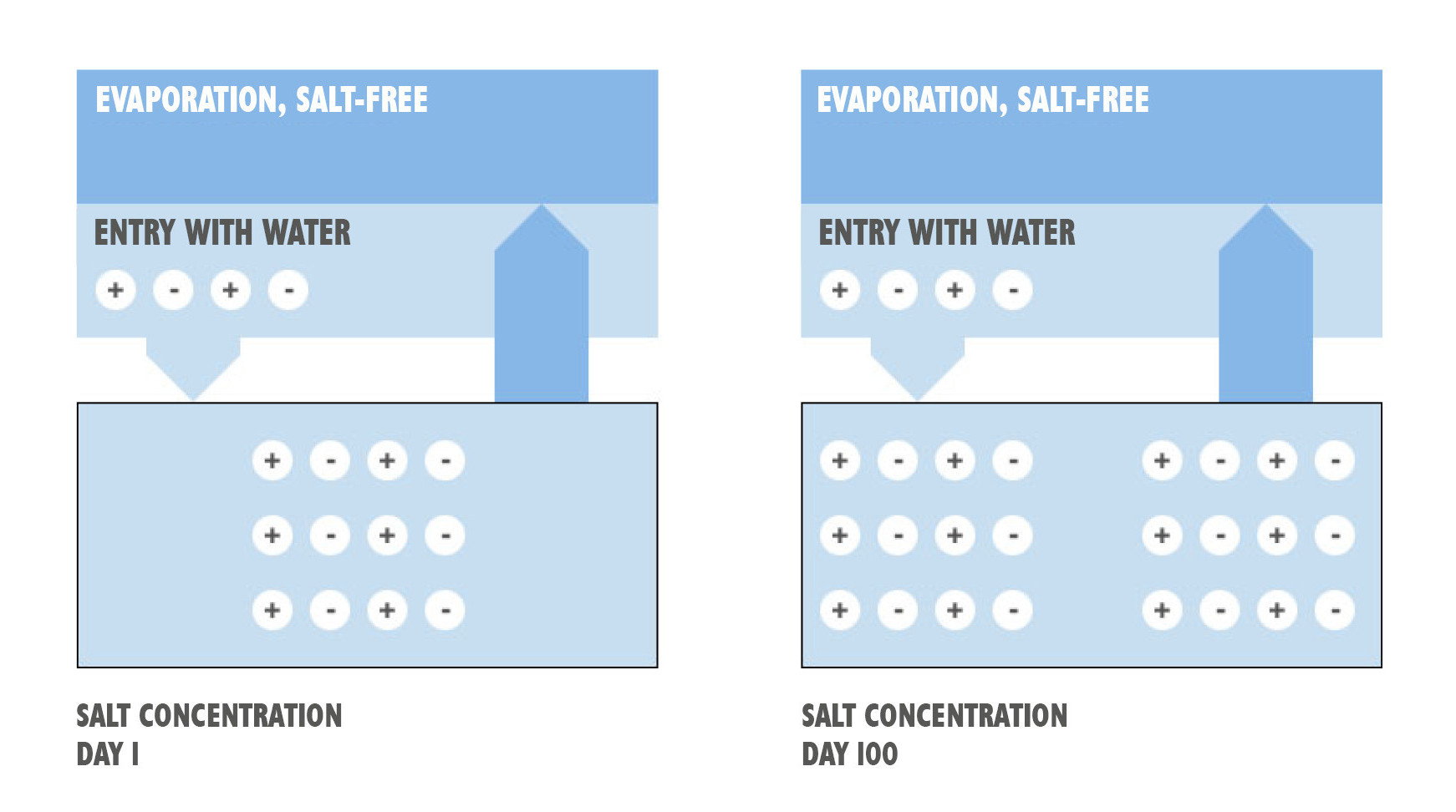
The faster evaporation of the tank volume also means a greater increase of the salts. So it may be that one high-performance machine requires more refill quantity than another with the same tank volume.
A drop test with the same coolant on Alu 7075 for a testing time of 12 hours gave the following result:
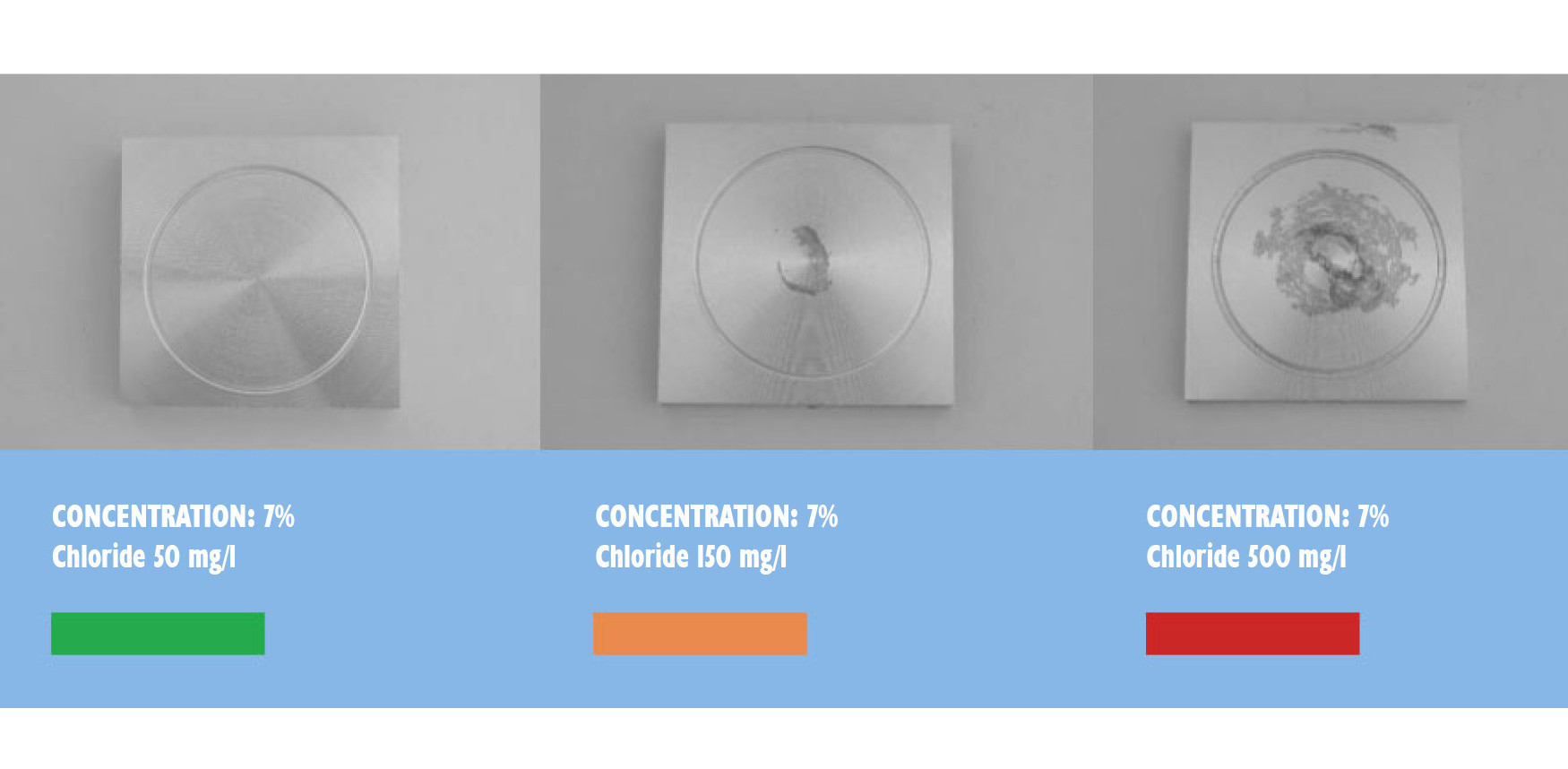
Residues disappear only by the use of demineralized water
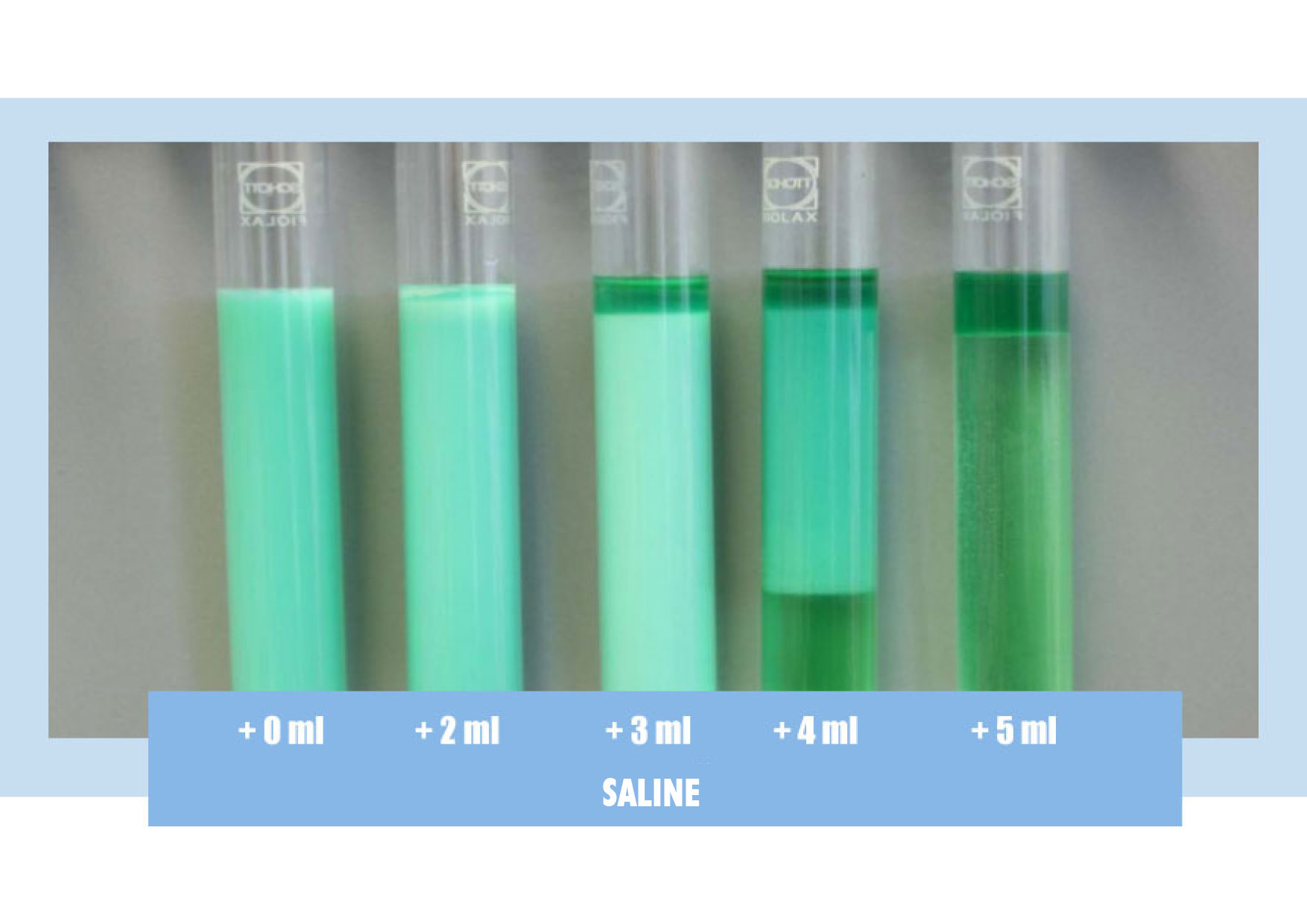
The graphics show the increase in salt concentration. After 68 days, chloride and sulfate continue to rise, but the hardness drops. This means that the substances are no longer bound. So the hardness is excreted as hard soaps.
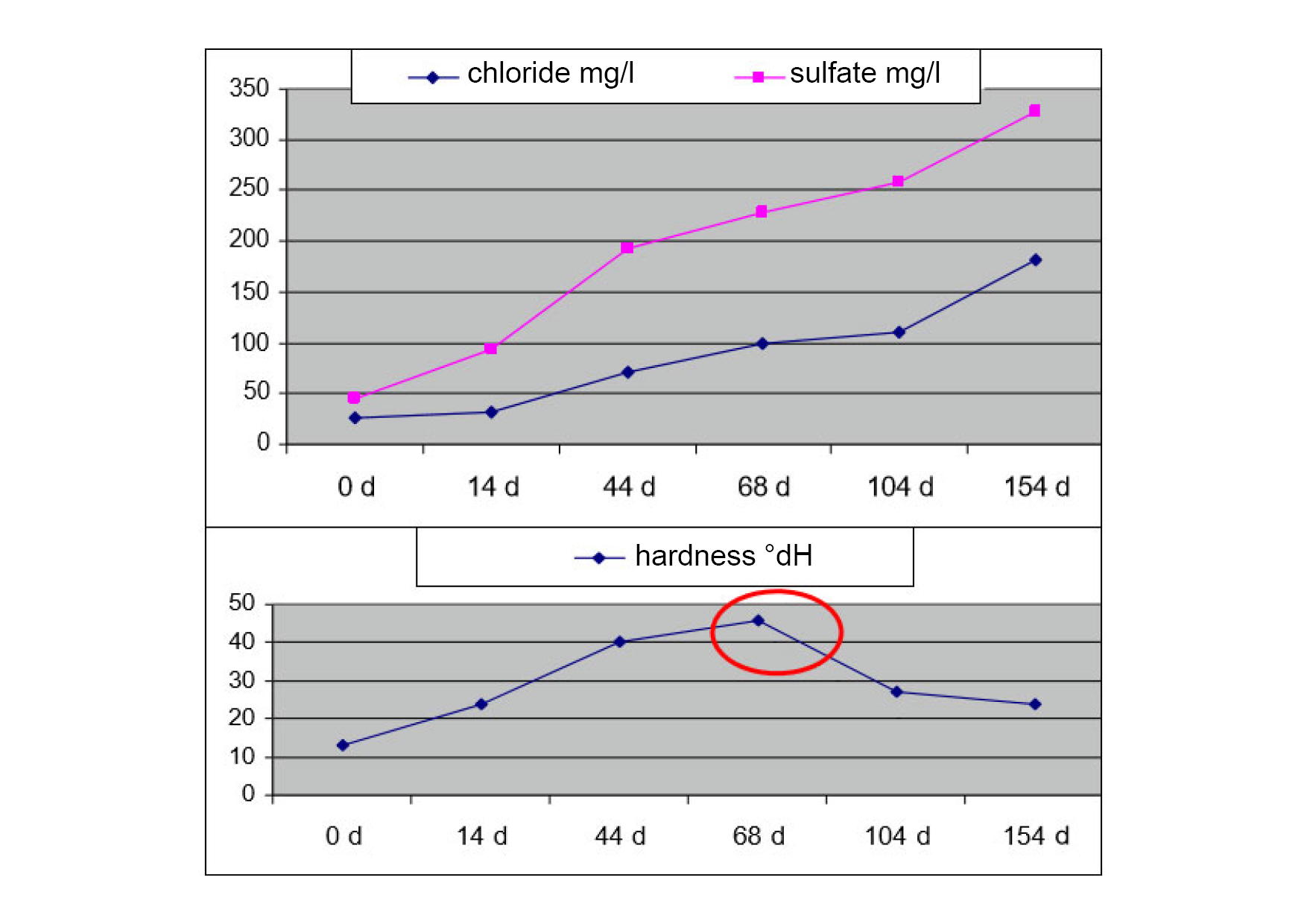
Mark: Hardness absorption capacity is exhausted
Advantages:
Disadvantage:
Recommendation:
For hard water and low chloride and sulphate values
Advantages:
Disadvantage:
Recommendation:
Good practice for industrial application
Advantages:
Disadvantage:
Recommendation:
For smaller consumption
You have any questions? Give us a call!
+49 (0) 85 71 / 79 70
